Axone is a public DPoS layer-1 specifically designed to enable communities to share data, algorithms, and resources to build the Dataverse. The network envisions the Dataverse as an open world where anyone can create or participate in custom ecosystems to build a new generation of dApps far beyond Decentralized Finance (DeFi).
The network enables the creation of fully customizable Data Spaces in which communities can agree on rules and collaborate with any digital resource - such as datasets, algorithms, and computation resources - to create new knowledge and applications.
So, let’s have a further look. Axone created a general-purpose ecosystem enabling XaaS (Anything as a Service) integration. Anything presented to the Protocol as a Service, regardless of what it does, where it is hosted or deployed, or who provides it, can be used by the Protocol. Herein lies the protocol's integration power, which provides infinite scalability and extensibility to the entire Axone ecosystem.
These typologies of service are already supported by Axone:
- Data as a Service - Data management services include storage, accessibility, and administration.
- Algorithm as a Service - Provides services that process data to generate meaningful information (i.e., knowledge), such as machine learning algorithms.
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) - refers to services that provide computation, storage, and networking resources.
- Identity as a Service - Services that provide decentralized identity management.
The Use Cases of the Dataverse
While there would be almost endless use cases for the Dataverse, Axone identifies four specific ones as their initial approach. The first is agricultural purposes. Agriculture is a market in which efficient information is vital to better evaluate, manage, and adjust business practices. With Axone's’s data solutions, crossing technical, harvest, and account data could generate unique new insights that might enhance results for the farmers and brands and provide transparency to end-consumers.
Then there’s the use case in which the Dataverse meets the Metaverse and its gaming ecosystem. As for now, the Metaverse is inextricably linked to Big Data. Metaverses pose a risk to data sovereignty and technological lock-in. If there was complete control over this data collection, according to the rules defined by the participants, the Metaverse could interconnect, passing information and data back and forth.
The third use case for the Axone Dataverse would be the supply chain. Data sharing can provide various benefits for companies, including cost reduction, improved collaboration, quality and efficiency of production, and risk management. By sharing data within the supply chain, companies can gain a more comprehensive understanding of their operations and the dynamics that govern them, enabling them to make more informed decisions and respond more effectively to challenges and opportunities. Data sharing can also facilitate the interoperability and coordination of systems, helping to overcome geographical, temporal, or informational distance and create a more collaborative environment. In addition, data sharing can help companies to identify and mitigate risks through the use of real-time monitoring and evaluation tools that can provide early warning of potential issues. Overall, data sharing can help companies to optimize their operations and create value for all actors in the supply chain.
A final use case example is that of NGOs in developing countries. By sharing data within a Data Space and thus the Dataverse, NGOs and other organizations can collaborate more effectively and share resources, knowledge, and expertise to address these challenges. In addition, the Data Space could provide processing services, such as format conversion and AI services, to help organizations analyze and interpret the data and make more informed decisions about where to prioritize interventions. By making the data available to both NGOs and companies for analysis or market research, the Data Space could also create opportunities for commercial collaboration and the development of new products and services to address these challenges.
KNOW, Axone’s Native Asset
KNOW is the Axone ecosystem's native currency that will enable value exchange. It is a mechanism that allows for the emergence of new types of networks and technologies that are not dependent on a single entity.
The Axone ecosystem will involve a large number of stakeholders. As mentioned above, users will use Data Spaces to store, share, exchange or access data and services to create knowledge via applications. There will also be validators and token holders who will ensure the blockchain's operation by providing nodes, delegating authority, and voting in the DAO. In the long run, the KNOW will incentivize all participants to contribute and become involved. The KNOW has multiple uses in the ecosystem:
- It will be the protocol's medium of exchange for initiating workflows and accessing applications.
- It will be used to become a validator with the ability to earn fees and block rewards.
- It will reward data, service, and infrastructure contributors. Contributors commit to the quality of their contribution by staking tokens to datasets and services they provide. In the event of fraud or failure to meet commitments, the governance can decide to reduce the stacked sum, thereby protecting users.
- Community members can stake tokens on datasets or services to signal the quality of their contribution to other members; users doing so are called curators.
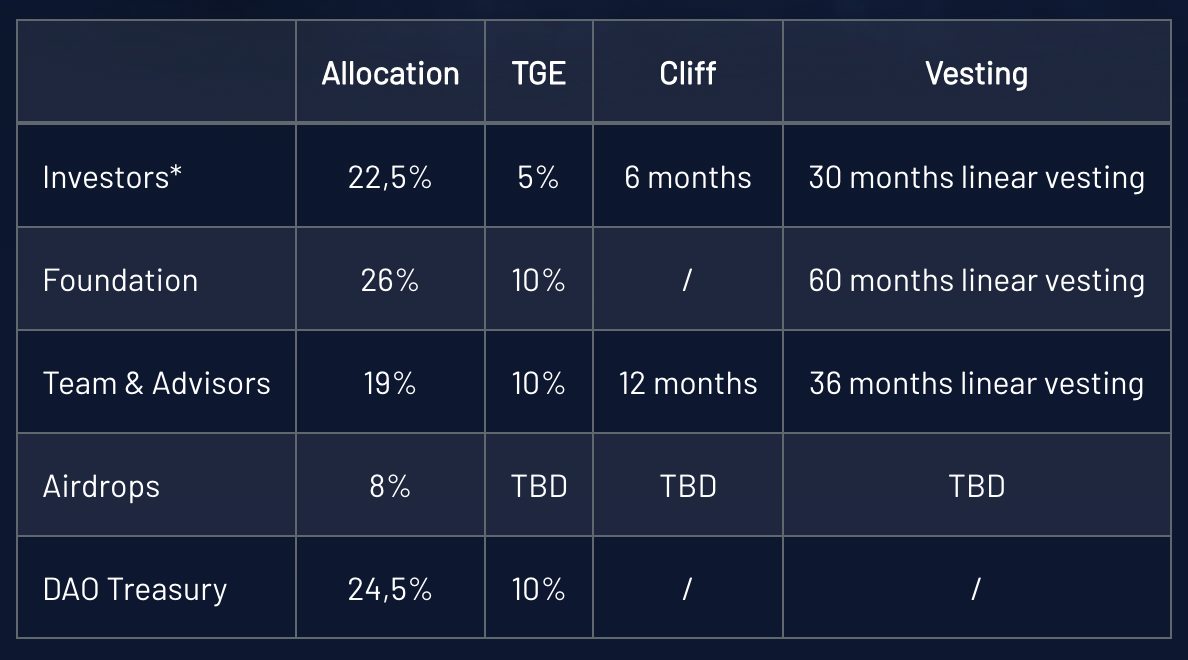
The total initial supply will be 200,000,000 $KNOW, and the maximum supply is 350,000,000 $KNOW (including block rewards, reached after 80 years).
Final Thoughts
Digital innovation has indeed had a significant impact on many aspects of society, including the way we exchange information and do business. The rise of data as a valuable resource has led to a growing focus on decentralized, peer-to-peer solutions for data exchange, as these can give users more control over their data and how it is used. Blockchain technology, in particular, can potentially enable the development of decentralized, secure, and transparent systems for data exchange, which can help increase trust and reduce the risk of data breaches or misuse. At Stakin, we’re excited to see how data solutions will continue to evolve within the blockchain ecosystem since this could help to drive further innovation and progress in the field.
DISCLAIMER: This is not financial advice. Staking, delegation, and cryptocurrencies involve a high degree of risk, and there is always the possibility of loss, including the failure of all staked digital assets. Additionally, delegators are at risk of slashing in case of security or liveness faults on some protocols. We advise you to do your due diligence before choosing a validator.



Join the conversation